Often the news around VR focuses heavily on gaming but VR and XR are going to shape our future in so many more ways than purely entertainment. From healthcare to real estate, recruitment, and education, this article covers 23 industries already using VR – and this is just the start.
For anyone who isn’t quite up to speed with VR, here’s a very brief definition: VR is the term used to describe a computer-generated environment that someone can explore and interact with. A user is immersed in the environment and the brain is basically tricked into thinking what someone is seeing in the virtual world is real.
1. Automotive industry
Virtual Reality (VR) is reshaping how the automotive industry handles vehicle design, engineering, and customer interaction. Major brands like Honda, BMW, and Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) use VR to conduct design and engineering reviews, significantly reducing the need for costly physical prototypes. This not only saves millions in man-hours and development costs but also enables global collaboration, allowing designers and engineers to work together across borders.

In the sales space, online retailers like Vroom offer virtual showrooms where customers can explore detailed 3D models of used cars, check their functionality, and even learn about their history. Automakers have also started launching new car models in virtual environments, using the metaverse to reach wider audiences and showcase their latest innovations without the constraints of traditional auto shows.
VR is also proving valuable in employee training. Companies like BMW are using VR to train staff on both technical and customer-facing skills, ensuring their teams are prepared for everything from vehicle design to delivering top-tier customer service. As VR continues to evolve, its role in the automotive industry—from design and prototyping to customer engagement and employee training—will only expand.
2. Healthcare
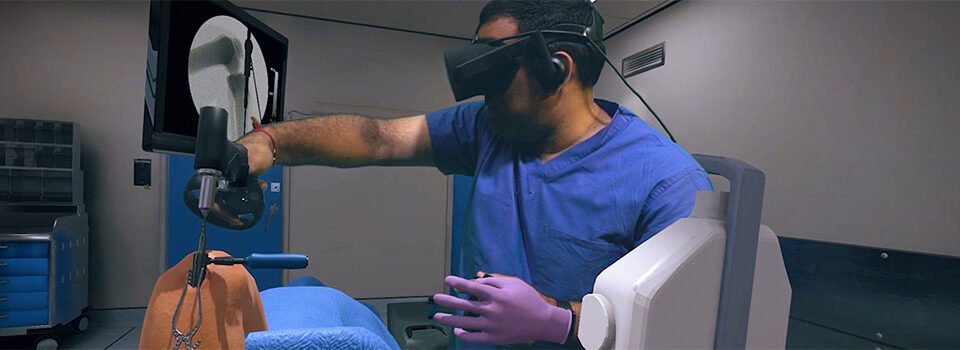
Virtual Reality (VR) is making a significant impact in healthcare, transforming both treatment and training. In November 2021, the FDA approved EaseVRx, a prescription-use VR system for chronic pain management. Using cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), deep relaxation, attention-shifting, and interoceptive awareness, the system helps reduce chronic pain in adults. VR has also been used effectively for pain relief in burn injuries, providing a non-invasive solution for pain management.

In surgical training, VR is proving invaluable. Companies like Osso VR allow surgeons to practice procedures in a virtual environment, interacting with medical devices and performing surgeries on virtual patients. This enhances their familiarity with new devices and improves their surgical proficiency. In the realm of diagnostics, companies like Altoida are developing extended reality (XR) platforms that leverage machine learning to identify digital biomarkers for neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s. These platforms allow for earlier diagnoses, better monitoring of disease progression, and greater participation in clinical trials.
VR can also be used as a treatment for mental health issues, with Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy thought to be particularly effective in the treatment of PTSD and anxiety. There are many other ways spending time in VR can have therapeutic benefits.

Moreover, VR is being used to help healthcare professionals practice delivering difficult news to patients with empathy. Through VR exercises, doctors can rehearse conversations such as delivering a serious diagnosis, explaining complex diseases, or discussing advanced care planning. These simulations provide feedback on communication skills, highlighting areas for improvement, and enabling doctors to refine their ability to handle emotionally charged conversations with compassion.
3. Retail
The way we shop online is set to drastically change with ‘the metaverse’. With VR retail experiences and body-scanning technology, we will be able to try on clothes in the virtual world to see what they’d look like in person. Not only is this a time-effective experience for shoppers, but it’s also more sustainable because customers will know before they order whether the item fits their shape and size, reducing the environmental cost of production and shipping fast fashion.
Various companies are attempting to bring us the VR shopping experience, including the European retailer ASOS, who invested in software development company Trillenium. The Metaverse now hosts it’s own fashion week, just like those hosted in New York and Paris.

Brands like Ralph Lauren and Gucci have also worked with VR Studio Emperia to make bespoke, virtual store environments for high end customers to browse their collection.
4. Tourism
The global pandemic and lockdowns accelerated a lot of developments in virtual travel, with many missing the freedom to travel to different countries, visit world-famous landmarks, and experience a glimpse into another culture.
In the post-Covid era, the developments in VR for tourism enable you to try a holiday before you buy it. Thomas Cook launched their ‘Try Before You Fly‘ VR experience all the way back in 2015, where potential holidaymakers could visit stores in various countries to experience the holiday in VR before booking it. As a result, there was a 190% uplift in New York excursions bookings after people tried the 5-minute version of the holiday in VR.

VR Expeditions 2.0 is another way tourism can become more accessible, with hundreds of virtual field trips available. From Rome’s Colosseum to coral reefs, and the surface of Mars, users can travel the world from the comfort of their own home.
5. Real Estate
If you’d prefer to stay closer to home, you can look around properties from the comfort of your [existing] home – no estate agent appointments or sacrificing your weekend needed.

Companies like Matterport are leading the way for people to explore houses online and get a ‘feel’ for the space, saving time looking rounds places that might be smaller, darked, or otherwise not what you expected. This way, you can focus your time viewing only the properties you’re most likely to love in person.
Besides, some companies like Stucco are using VR for home staging. This doesn’t only save costs but also allows real state agents to use different interior design styles depending on the client’s preferences.
6. Architecture
Virtual Reality (VR) is transforming how architects design and visualize spaces, offering a more immersive and interactive way to experience buildings before they are constructed. By stepping into a 3D virtual environment, designers can explore spaces, materials, and lighting as though they were physically present, enabling more accurate and efficient design decisions. Real-time changes can be made, allowing architects and clients to collaborate closely and refine projects during the design phase.
For example, Foster + Partners used VR to design the Bloomberg European Headquarters in London, allowing architects and clients to walk through the virtual building and make adjustments before finalizing the design.
VR also benefits homeowners looking to renovate or extend their properties. They can experience and visualize what the space will look and feel like before construction begins, making adjustments as needed. This not only saves time and money but also increases customer satisfaction by ensuring the final result aligns with their expectations. This approach is even featured in popular media, such as the UK TV show Your Home Made Perfect, where rival architects present VR designs to homeowners before the physical work starts.
7. Interior design
VR is not only revolutionizing architecture but also transforming the world of interior design. With immersive experiences, homeowners and designers can visualize every detail of a room—from lighting and ventilation to color schemes and furniture placement—before making any changes in real life.
Companies like Flipspaces are at the forefront of this trend, offering 3D visualizations of interiors that help users get a feel for their home or workspace layout, making real-time adjustments as they explore. These platforms also provide a direct sales boost to furniture companies, as users can experiment with specific products within the virtual space.
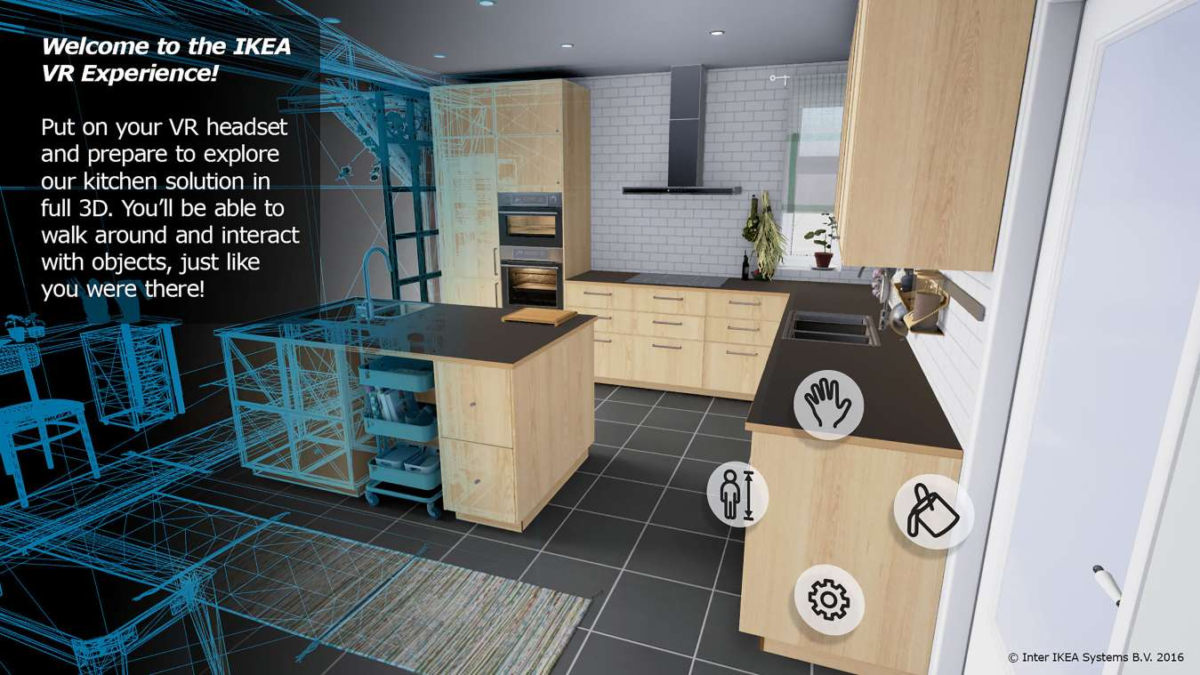

Ikea, for instance, has developed a VR app that lets users visualize furniture within a virtual environment. Imagine planning a kitchen renovation on a budget, unsure of what materials, colors, or styles to choose. Instead of hiring a designer, you can open the Ikea VR app and experiment yourself. In the virtual kitchen, you can change the colors and finishes of cabinets, swap countertops, and even place pots and pans on the stove. This hands-on experience helps users make informed design decisions, creating a more satisfying and cost-effective renovation process.
8. Gambling
Fancy yourself as a poker pro? You can play multiplayer poker in VR with Vegas Infinite, formerly Pokerstars VR. It’s just like being in a real casino where you can talk to other players and read their body language. You can plan poker, blackjack, roulette, and slots against real opponents and be in with the chance of winning money prizes.
9. Learning and development
The training industry has started to embrace the opportunities VR learning brings, with companies like Bank of America sourcing 10,000 headsets, and Walmart offering VR training to its 1mn employees.
With VR, people can learn through experience in a risk-free space; it’s consistent, affordable, and scales. VirtualSpeech, for example, provides VR training for soft skills such as public speaking, active listening, and sales. They blend e-learning with practice in VR and online simulations, enabling learners to build their confidence and skills in VR environments, from meeting rooms to auditoriums.
With the experiential learning VR brings, VR training significantly increases learning retention levels PwC infamously did a study on the effectiveness of VR learning for soft skills, and found people learnt up to 4 times faster in VR.

Learn and practice communication skills with VirtualSpeech.
10. Recruitment
Lloyds Banking Group became the first organization in the UK to introduce VR exercises to assess graduates for its 2017 intake. In the future, VR could be used to assess key skills required for a job such as decision making, for job interviews, and could even replace assessment days altogether by bringing candidates together in the metaverse.
This would save both the employer and potential employee time and cost in the interview process, and even attract higher quality candidates, as Deutsche Bahn has found.
11. Entertainment
VR is being used in the entertainment industry to heighten experiences with 360 films (Examples on YouTube) and increase emotional connection with the characters or film itself. Disney Movies VR, for example, takes the user to red carpet events and to an interview with ‘The Jungle Book’ cast.
VR could also revolutionize the way that media content is made, as companies like Flipside XR have shown. Flipside provides real-time animation and motion capture, enabling creators to built interactive animated shows or live stream animated performances via VR or more traditional channels YouTube, Twitch or Facebook live.
12. Education
VR is revolutionizing education by enabling students to learn in an immersive, experiential way, from anywhere in the world. VR provides the opportunity to democratize education by opening up opportunities to students of all backgrounds, which may not have been possible before.

For example, Victory XR has partnered with Engage to provide digital twin campuses to enable students to learn in live, interactive classes from the brightest minds in the world. Another example of VR in Education is the RTC Antwerpen project, the largest XR education initiative to date, which will equip 150K students across 690 schools with immersive learning opportunities.
Other companies like Tech Row enable students to go on a space mission to Pluto, explore Antarctica, and experience the wonders of Machu Picchu. Field trips to the Colosseum and Ancient Rome can be completed from the classroom, and you can even be taken on a journey of the human body as a white blood cell!
13. Sports
The way that we watch sports is already changing, with several VR companies specializing in watching live sports events. You can now watch the NBA, NFL, and other events in VR. BT Sport broadcasted the UEFA Champions League final in 360 degree VR via YouTube and the BT VR app, all for free. You could watch the game from several viewpoints in the stadium, as if you were actually there.
Companies such as Big Screen VR enable people to watch the Superbowl together in VR, and NBC announced it will live stream the opening and closing ceremonies of the Beijing Olympics in VR, as well as provide highlights for some of the events in VR. You can even host a ‘virtual Olympics watch party‘ if that’s your kind of thing.
This is a great way of opening up live sports events to people who can’t travel to the venue or can’t afford tickets to watch the sports in person. Instead, they can get a sense of atmosphere and presence from VR.
14. Art and design
With VR, you don’t just create life-size artwork – you can be in it. You can actually step into your image and come out the other side. The most well-known application for creating art in VR is Tilt Brush and it’s amazing what some people have managed to paint in it. You can also draw, sculpt, create and animate virtual 3D models and sculptures with Masterpiece Studio.

One of VR artist Anna Zhilyaeva’s incredible pieces of art, created with Tiltbrush.
15. Events, conferences and meetings
Since VR enables individuals to meet in places virtually, it’s no surprise that the pandemic brought a rise in VR events, conferences, and meetings. Platforms such as Remio VR, Rec Room, and Horizon Workrooms can be used to hold collaborative, interactive meetings with colleagues from anywhere in the world.
You can put on your headset in London, and meet virtually with your colleagues in New York and Madrid, and connect and work with them as if you were all in the same room. With collaboration tools such as whiteboards and freehand 3D drawings, they help remote or hybrid meetings become as good as face-to-face meetings, without the time and cost needed to travel.
Some people are using VR for networking and events. Educators in VR regularly host events in VR on topics including cyberbullying, storytelling, and language learning, which are available to attend in VR or desktop. By bringing people together in VR, attendees can immerse themselves in the topic and virtual space, and build stronger connections with each other compared to events via traditional video conferencing tools.
16. Fitness
When we first wrote this article in 2017, VR fitness wasn’t a thing – we originally had 21 industries using VR and fitness wasn’t one of them. Now, VR fitness apps are some of the most downloaded and used VR apps available, allowing you to upgrade and socialize your home workout.
Two of the most popular VR fitness apps are Supernatural and Fit XR. With FitXR, for example, you join an immersive fitness club with new classes added each day, including boxing, dance, and HIIT. You can even take part in the classes live with your friends to make your workout even more fun, and mimic the social interaction of traditional gym classes. Another use case of VR in fitness is wearing the headset while being on a static bike. Apps like Vzfit and Holofit allow you to bike through real locations or virtual worlds from the comfort of your own home.
17. Wellbeing
With the growing popularity of wellness and meditation, it’s no surprise that you can now meditate in VR. Companies like TRIPP are leading the charge, offering over 40 meditations, breath visualizations, and calming visual landscapes designed to help users achieve a more peaceful state of mind. Available for VR and soon for AR, TRIPP promotes itself as a “fitness solution for your inner self,” providing an immersive escape into a serene virtual environment that enhances relaxation.

In the therapeutic space, XRHealth is transforming patient care by leveraging VR for mindfulness and relaxation in clinical settings. Their experience Space platform uses AI to enhance mental health support and physical and cognitive therapies. Through these VR therapy solutions, patients can engage in mindfulness exercises while healthcare professionals gain innovative tools to improve patient outcomes.
Together, platforms like TRIPP and XRHealth are pioneering the integration of VR into the wellness and therapeutic landscape, helping users find inner calm while also advancing clinical care.
18. Social
VR enables people to meet in the same virtual space from anywhere in the world. Once in VR, or ‘the metaverse’, people can visit virtual cinemas, restaurants, beaches, concerts, and more together.
There are several big players already building social communities in the VR space, including Meta’s Horizon Worlds and AltspaceVR. Horizon Worlds not only enables people to explore virtual worlds together, but they can create immersive content too, including VR spaces specifically for their friends and colleagues.
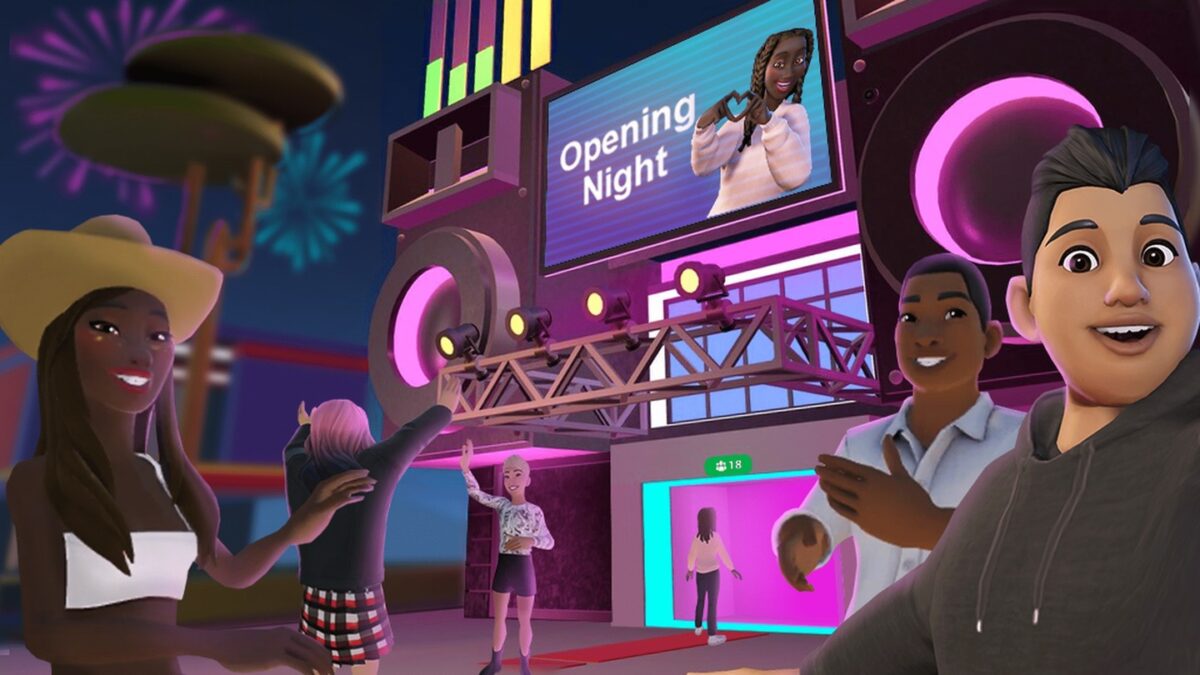

Horizon Worlds, Meta’s social VR app
19. Charity
One of the best things about the rise of VR is its ability to evoke empathy. This makes it extremely valuable to charities as it can be used to increase understanding of an issue by experiencing it either in the first person or as a bystander to specific situations.
People are more likely to be moved to action when they are immersed in a situation, they would otherwise not be able to relate to, or come close to experiencing. For example, in 2015, Unicef used the video ‘Clouds Over Sidra‘ to double their donations towards their work with the Syrian Refugee Crisis. Another example of this is the “A walk through dementia” VR experience. Created by Alzheimer Research UK, this experience walks users through the heartbreaking reality of what having Alzheimer’s is like.
20. Marketing
Marketing is becoming more and more about how companies make customers feel so utilizing the immersion of VR seems like a natural extension. From Topshop providing fashionistas with a front row at London Fashion Week with a VR headset, to Tom’s shoes taking customers on a trip through Peru to show where each pair of shoes they donate goes to, the heightened sense of connection through VR is sure to make you remember and connect with these brands.
VR marketing is also becoming popular for universities to create virtual campus tours of universities. Princeton, Yale, and Columbia have all tried this out as a way for more students to be able to see their campus.
21. Recreation
Many real-life hobbies are now available in VR, and the immersive, social experience makes them all the more enjoyable and accessible. If you’re a fan of cultural activities, you can visit museums such as the Natural History Museum in London or if you’re into sports, you can play golf or football in VR.

If you’re more of a thrill-seeker, you can head to Guizhou in China to VR Star Theme Park, where there are over 40 VR rides.
22. Law enforcement
As with the military, police forces are using AR and VR tools from companies like VirTra to train personnel in simulated scenarios complete with visual, auditory, and physical stimuli (ranging from barking dogs and street noise to the recoil of discharging a weapon).
The technologies even enable police forces to escalate or de-escalate trainees’ simulated interactions with individuals inside the virtual training environments, helping learners practice making judgment calls and critical decisions under stress.
A group of University of Alabama researchers had collaborated with law enforcement officials to measure brain waves during VR police training. One of the lead researchers said the work may “improve training of officers and positively affect the hiring process.”

23. News and journalism
You can now watch news stories and documentaries in VR. The New York Times has already entered this space, and it’s only a matter of time before other media outlets join them. In the NYT VR app, you can experience stories rather than just listen to them, as if you were standing opposite the journalist where the story is happening.
Virtual Reality is poised to reshape not only our workplaces but also our hobbies and social lives—perhaps sooner than we imagine. The possibilities with VR are vast, allowing us to interact, learn, and create in ways once thought impossible. While we can’t replace basic human experiences like eating and sleeping in VR just yet, the technology’s rapid evolution suggests that the future holds even more groundbreaking potential.